03 Nov Environmental Monitoring System vs. Building Management System
The desire for sustainability and effective resource management in modern society has resulted in the creation and deployment of a variety of systems targeted at monitoring and managing the environment inside buildings. Environmental Monitoring System and Building Management System are two critical systems that play an important role in this respect. These systems are frequently interconnected yet perform diverse functions. In this article, we will look at the technical features of these systems, as well as their distinctions and uses.
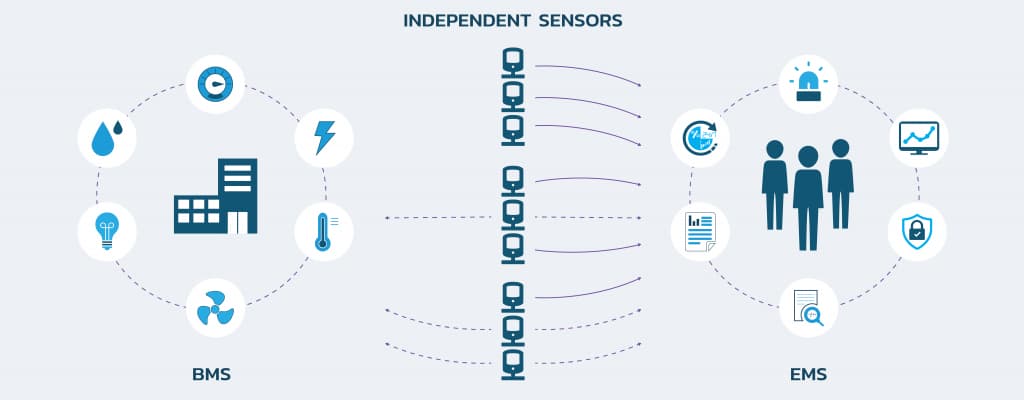
Environmental Monitoring System (EMS)
An Environmental Monitoring System (EMS) is a system that monitors and manages the environmental factors within a building or specified region. To provide a pleasant and healthy interior environment, this system focuses on characteristics such as moisture, temperature, air quality, and illumination. Let us now examine the technical features of EMS.
Sensors and Data Collection: EMS collects real-time data on environmental conditions via a network of sensors. Thermal sensors, moisture sensors, carbon dioxide detectors, and light sensors are examples of these sensors. The information collected is critical for sustaining the appropriate interior atmosphere.
Data Analysis and Processing: After collecting the data, it goes through processing and analysis to determine the environmental conditions. Complex algorithms may be employed to evaluate if air quality, humidity, and temperature are within acceptable limits.
Control Mechanisms: Based on data and analysis, EMS may automatically modify heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, as well as lighting. If the temperature increases beyond a certain threshold, for example, the system can order the HVAC system to cool the space.
Alarms and Notifications: If environmental conditions vary from an acceptable range, EMS can send alarms and notifications to the building operators or facility managers. It enables rapid reactions to possible problems.
Building Management System (BMS)
A Building Management System (BMS) or Building Automation System (BAS) has a greater scope than an EMS. It is in charge of regulating and monitoring a variety of building systems, such as the HVAC system, lighting, safety, and energy management. Let us now look at the technical features of BMS.
System Integration: Building management systems (BMS) combine diverse building systems into a consolidated platform. The use of a network of sensors, controls, and software applications accomplishes this. BMS, for example, may regulate HVAC, lighting, and safety measures all at once.
Control Logic and Automation: Building management systems (BMS) employ advanced control logic to automate the functioning of building systems. Specific criteria or triggers can be encoded into the logic. For example, when the facility is empty, the BMS may turn down the HVAC and lighting to conserve energy.
User Interfaces: Building management systems (BMS) provide user-friendly interfaces, which are frequently available via computers or mobile devices, allowing building managers to monitor and operate different systems. These interfaces allow for continuous tracking, scheduling, and reporting.
Energy Efficiency: BMS is critical to optimizing energy consumption. It can monitor energy use and discover energy-saving possibilities by altering systems based on occupancy and ambient factors.
Key Differences
As we’ve covered the technical features of both systems, let’s compare and contrast EMS and BMS.
Scope: The primary emphasis of EMS is to monitor and regulate environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and air quality. The scope of BMS, on the other hand, is greater, comprising HVAC, lighting, safety, and energy management.
Integration: EMS is primarily used as a stand-alone system for environmental monitoring. The building management system (BMS) connects numerous building technologies, creating a consolidated platform for building administration.
Control Logic: BMS automates building systems with complex control logic, whereas EMS focuses on sustaining specified environmental conditions. The control logic of a BMS frequently uses environmental data from an EMS.
User Interfaces: BMS provides simple user interfaces that enable building operators to handle many systems from a single location. For environmental monitoring and control, EMS interfaces are more specialized.
Applications
Both EMS and BMS have specific uses and may be utilized in a variety of circumstances. Understanding their applications is essential for making sound selections about which system to deploy.
Applications of Environmental Monitoring Systems (EMS)
Laboratories: Environmental monitoring systems (EMS) are critical for maintaining accurate environmental conditions in research and medicinal laboratories.
Data Centers: To secure sensitive equipment, data centers need accurate temperature and humidity management.
Clean rooms: Industries such as semiconductor production rely on EMS to keep clean-room conditions consistent.
Hospitals: Air quality and temperature management in hospitals are crucial for the comfort of patients and infection control.
Applications of Building Management Systems (BMS)
Commercial Buildings: Building management systems (BMS) are extensively employed in office buildings to enhance energy efficiency, security, and customer comfort.
Industrial Facilities: BMS is used in industrial plants to control HVAC, lighting, and security systems efficiently.
Retail Spaces: BMS assists merchants in maintaining optimal shopping conditions while lowering energy expenditures.
Educational Institutes: Schools and colleges can use BMS to regulate ambient conditions, lighting, and security.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Environmental Monitoring System and Building Management System are critical in the maintenance and management of the environment within buildings. EMS is primarily concerned with monitoring and managing environmental conditions, whereas BMS integrates and contains a larger variety of building systems. Understanding the technical elements and uses of these systems is critical for selecting the best option to satisfy specific building needs. Whether it’s an academic institution, laboratory, data center, office building, or industrial facility, the extent of control and management required to maintain ideal interior conditions and resource efficiency will determine which system to choose.




Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.